19 Things you should know about Smartwatch
“Navigate the world of smartwatches, understand their features and uses, and make an informed choice with our smart buying guide. Uncover the future of wearable tech.”

Definition of Smartwatch
A smartwatch is a wearable electronic device that combines the functionality of a traditional wristwatch with advanced digital features. It goes beyond simply telling time, offering a wide range of capabilities such as communication, health monitoring, app integration, and more. Smartwatches are designed to be worn on the wrist and connect seamlessly with smartphones and other devices, enhancing the user’s convenience and productivity
1. Features of Smartwatch
Notifications: Displaying calls, messages, and app alerts.
Fitness Tracking: Monitoring steps, heart rate, sleep, and more.
Apps: Running various applications, from weather updates to social media.
Communication: Making calls and sending messages.
Health Monitoring: Tracking health metrics like ECG, SpO2, and stress levels.
Navigation: Providing GPS navigation and outdoor activity tracking.
Customization: Personalizing watch faces and settings.
Voice Commands: Interacting with voice assistants for hands-free tasks.


2. Differences from Traditional Watches
Smartwatches differ from traditional watches in several ways:
Functionality: Smartwatches offer advanced features beyond timekeeping, while traditional watches focus solely on telling time.
Connectivity: Smartwatches are capable of connecting to smartphones and other devices, enhancing their functionality.
Interaction: Smartwatches feature touchscreens, buttons, and voice control, enabling interactive communication and tasks.
Notification Center: Smartwatches display notifications, allowing users to stay connected without accessing their phones.
Activity Tracking: Unlike traditional watches, smartwatches can track activities, heart rate, sleep, and more for health insights.
Apps and Customization: Smartwatches support apps and offer customization options like interchangeable watch faces.
Integration: Smartwatches integrate with digital assistants and provide data syncing with smartphones.
3. Components of a Smartwatch
Display Types
Smartwatches feature various display types that impact visual quality and energy efficiency:
LCD (Liquid Crystal Display): Offers vibrant colors and visibility in sunlight. Energy-efficient.
OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode): Provides deep blacks, vibrant colors, and energy efficiency by lighting individual pixels.
AMOLED (Active Matrix OLED): Combines OLED with active matrix technology for improved response times and image quality.
Touchscreen Functionality and User Interfaces
Smartwatches often incorporate touchscreens for intuitive interaction:
Touchscreens: Enable navigation through menus, swiping, tapping, and gestures.
Gestures: Some support pinch-to-zoom and scrolling gestures.
User Interfaces: Designed for smaller screens, featuring icons and layouts optimized for easy use.
Buttons, Bezels, and Navigation Methods
Smartwatches offer various navigation methods beyond touchscreens:
Physical Buttons: Perform tasks like accessing the home screen, returning, or launching apps.
Rotating Bezels: Some have a rotating bezel for scrolling through menus and notifications.
Digital Crown: Turned and pressed for navigation and zooming (on certain models).
Sensors
Sensors are crucial for smartwatch functionalities:
Heart Rate Sensor: Measures heart rate for fitness tracking and health insights.
GPS (Global Positioning System): Provides location tracking for outdoor activities and navigation.
Accelerometer: Detects motion and orientation for steps, activities, and gestures.
Gyroscope: Works with the accelerometer for orientation and movement detection.
Ambient Light Sensor: Adjusts display brightness based on lighting conditions.
Barometer: Measures atmospheric pressure for altitude and weather data.
SpO2 Sensor: Measures blood oxygen levels for health assessment.
Connectivity Options
Smartwatches offer various connectivity options for communication:
Bluetooth: Common for pairing with smartphones and devices.
Wi-Fi: Connects to Wi-Fi networks for data syncing and updates.
NFC (Near Field Communication): Enables contactless payments and device pairing.
Cellular Connectivity: Some have cellular capabilities for calls, messages, and internet access.


4. Operating Systems ( OS ) for Smartwatches
Each smartwatch OS offers unique features and interfaces tailored to their ecosystems
Wear OS
Google Assistant integration for voice commands.
Extensive app selection from the Google Play Store.
Customizable watch faces and complications.
Integration with Google services like Gmail and Maps.
WatchOS
Deep integration with Apple ecosystem.
Diverse watch faces, including animated options.
Taptic Engine for haptic feedback, Digital Crown for navigation.
ECG and fall detection features for health monitoring.
Tizen
Circular app layout and rotating bezel navigation (on some models).
Variety of watch faces, apps, and widgets.
Health features like heart rate and stress monitoring.
Integration with Samsung devices and services.
Fitbit OS
Fitness-focused with continuous heart rate monitoring.
Guided workouts and personalized fitness coaching.
Integration with Fitbit app and community.
Garmin Connect IQ
Custom data fields and specialized apps for outdoor activities.
Activity profiles for various sports and adventures.
GPS and navigation features for accurate tracking.
Huawei LiteOS
Energy-efficient design for extended battery life.
Integration with Huawei smartphones.
Health tracking features, including heart rate monitoring.
5. History & Evolution of Smartwatches
Brief History of Smartwatches and Their Evolution
The concept of smartwatches traces back to the 20th century, but modern smartwatches have evolved significantly:
1970s-1980s: Basic digital watches with calculator and gaming functions emerged.
1990s: Watches added phone directories and calendar features.
Early 2000s: Microsoft introduced SPOT, allowing data reception via FM signals.
2010s: Major developments reshaped the landscape:
2013: Samsung’s Galaxy Gear marked the start of modern smartwatches.
2014: Google introduced Android Wear (now Wear OS).
2015: Apple Watch debuted with app ecosystem and iPhone integration.
2018: Health monitoring took center stage, focusing on heart rate and sleep tracking.
Milestones and Key Advancements
Several milestones shaped smartwatch evolution:
Touchscreens: Capacitive touchscreens revolutionized interaction.
App Ecosystems: Apple Watch App Store and Google Play Store added diverse apps.
Health and Fitness: Smartwatches became health companions with heart rate, ECG, and sleep tracking.
Cellular Connectivity: Cellular-capable smartwatches gained independence.
Customization: Bands and watch faces allowed personalization.
Battery Efficiency: Improved battery life extended usage.
Voice Assistants: Integration of voice assistants like Siri and Google Assistant.
Fashion and Design: Partnerships introduced stylish designs.
Future Trends
Anticipated trends in smartwatches’ future include:
Health Focus: Advanced health monitoring and medical-grade sensors.
Wearable Ecosystems: Integration with wearables for comprehensive health insights.
Form Factor Innovation: Flexible displays and new designs.
AI and Personalization: AI-driven insights and tailored recommendations.
IoT Integration: Better integration with smart homes and devices.
Battery Life Improvement: Enhanced efficiency without sacrificing features.


6. Smartwatch Use Cases
Fitness Tracking and Health Monitoring Features
Smartwatches serve as valuable tools for health and fitness:
Activity Tracking: Monitor steps, distance, and calories burned.
Heart Rate Monitoring: Continuously track heart rate for fitness insights.
Sleep Tracking: Analyze sleep patterns and quality.
Stress Monitoring: Measure stress levels and offer relaxation exercises.
Blood Oxygen (SpO2) Monitoring: Assess blood oxygen saturation levels.
Notifications and Communication Capabilities
Smartwatches keep users connected on the go:
Call and Message Notifications: Receive call and message alerts.
Quick Replies: Respond with preset messages or voice-to-text.
Email Notifications: Preview and receive email alerts.
Social Media Alerts: Stay updated with social media notifications.
Smart Home Integration and Control
Smartwatches enhance home automation:
Home Automation: Control smart devices like lights, thermostats, and locks.
Voice Control: Issue voice commands to control smart home devices.
Navigation and GPS Functionalities
Smartwatches assist with navigation and location-based tasks:
GPS Navigation: Track outdoor activities and receive accurate location data.
Turn-by-Turn Directions: Get navigation guidance while walking or cycling.
Entertainment Features (Music Playback, Apps, Games)
Smartwatches offer entertainment on the wrist:
Music Playback: Store and play music without a smartphone.
App Ecosystem: Access various apps for tasks and activities.
Gaming: Enjoy simple games and puzzles on the watch.
7. Compatibility & Pairing
Compatibility with Smartphones and Other Devices
Smartwatch compatibility ensures seamless integration:
Smartphone Compatibility: Smartwatches are designed for specific operating systems (OS). For instance, Wear OS pairs with Android, while watchOS pairs with iPhones.
Ecosystem Integration: Compatibility guarantees optimized features and functions within the chosen ecosystem.
Pairing Methods and Requirements
Pairing establishes a connection between devices:
Bluetooth Pairing: Common method, requiring Bluetooth on both devices.
Steps: Enable Bluetooth, access watch settings or companion app, select watch name, enter a pairing code.
App Installation: Some need companion apps on smartphones for setup.
QR Code or NFC Pairing: Scanning QR codes or using Near Field Communication simplifies pairing.
OS-Specific Methods: Specific OSs may have tailored pairing methods.
Example: Apple Watch pairs through the Apple Watch app on iPhones.
Requirements for Pairing
Successful pairing necessitates specific conditions:
Compatible Devices: Ensure compatibility between smartwatch OS and smartphone OS.
Bluetooth: Both devices must have Bluetooth capability.
Updated Software: Update OS and firmware for smooth pairing.
Stable Internet: Active internet for app download and updates.
Battery Life: Sufficient charge on both devices during pairing.


8. Battery Life & Charging
Factors Affecting Battery Life
Battery life is influenced by several factors:
Usage Patterns: Intensive app use and frequent notifications drain battery faster.
Screen Brightness: High brightness consumes more power.
Connectivity: Constant Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, or cellular connection affects battery life.
Sensors: Active sensors like heart rate and GPS consume energy.
Display Type: OLED displays consume less power for darker content.
Background Processes: Background apps and processes impact battery life.
Battery Size: Larger batteries offer extended usage.
Different Charging Methods
Smartwatches offer various charging options:
Cable Charging: Most common method involves connecting a charging cable to the watch’s port.
Wireless Charging: Uses magnetic induction to charge the watch wirelessly.
Dock Charging: Placing the watch on a charging dock or stand.
Solar Charging: Some watches feature solar panels for supplementary charging.
Battery Packs: Portable battery packs for charging on the go.
9. Customization and Watch Faces
Ability to Customize Watch Faces and Designs
Smartwatches offer customization options to match personal preferences:
Watch Faces: Users can choose from a variety of watch face designs.
Interchangeable Bands: Changeable bands allow for different styles.
Widgets and Complications: Display useful information on the watch face.
Availability of Third-Party Watch Face Apps
Smartwatch platforms provide access to third-party watch face apps:
Diverse Selection: Users can download watch faces from app stores.
Personalization: Find watch faces to match individual interests and styles.
Features: Some watch faces offer complications, animations, and dynamic elements.
Third-party watch faces enhance personalization, allowing users to tailor their smartwatch experience to their preferences.


10. App Ecosystem
Overview of App Stores and Available Apps for Smartwatches
Smartwatches have their own app stores offering a range of apps for enhanced functionality:
Apple Watch App Store: For watchOS devices, featuring apps designed specifically for the Apple Watch.
Google Play Store for Wear OS: Catering to Wear OS devices, offering apps compatible with Android-based smartwatches.
Galaxy Store: Samsung’s app store for Tizen-powered Galaxy smartwatches.
Fitbit App Gallery: Home to apps designed for Fitbit smartwatches.
Garmin Connect IQ Store: Providing apps for Garmin smartwatches.
Huawei AppGallery: Offering apps for Huawei LiteOS-powered watches.
Examples of Popular App Categories
Smartwatch app stores offer a diverse range of app categories:
Fitness and Health: Apps for tracking workouts, monitoring heart rate, counting steps, and managing health goals.
Notifications and Communication: Apps for receiving and responding to messages, calls, and social media notifications.
Productivity: Apps for setting reminders, managing to-do lists, and accessing calendars.
Weather: Apps that provide current weather conditions and forecasts.
Navigation: Apps with GPS capabilities for navigation and mapping.
Entertainment: Apps for music playback, podcasts, audiobooks, and games.
Finance: Apps for managing budgets, tracking expenses, and even making mobile payments.
News and Information: Apps delivering news headlines, updates, and customized content.
11. Health and Fitness Features
Heart Rate Monitoring and ECG Capabilities
Smartwatches contribute to health monitoring through heart rate measurements:
Heart Rate Monitoring: Continuously tracks heart rate throughout the day.
Resting Heart Rate: Provides insights into cardiovascular health.
Heart Rate Zones: Alerts users when heart rate exceeds or falls below target zones.
ECG (Electrocardiogram): Some watches offer ECG capabilities to detect irregular heart rhythms.
Sleep Tracking and Analysis
Smartwatches assist in optimizing sleep patterns:
Sleep Tracking: Monitors sleep duration and sleep stages.
Sleep Analysis: Provides insights into sleep quality and patterns.
Wake-Up Alarms: Gently wakes users during optimal sleep phases.
Fitness Tracking (Steps, Distance, Calories, etc.)
Smartwatches encourage an active lifestyle through fitness tracking:
Step Count: Measures daily steps taken.
Distance Traveled: Calculates distance covered.
Calorie Burn: Estimates calories burned during activities.
Active Minutes: Tracks time spent in active pursuits.
Workout Modes and Guided Exercises
Smartwatches offer diverse workout features:
Workout Modes: Choose specific activities (running, cycling, swimming, etc.) for accurate tracking.
GPS Tracking: Provides route and distance information for outdoor activities.
Guided Exercises: Some watches offer on-screen instructions for guided workouts.
Workout Analysis: Review workout stats and progress.


12. Communication and Notifications
Notifications from Smartphones (Calls, Messages, Emails)
Smartwatches enhance communication by relaying notifications from smartphones:
Call Notifications: Displays incoming call information.
Message Notifications: Alerts for incoming text messages.
Email Notifications: Shows email subject lines and senders.
Quick Replies and Voice-to-Text Features
Smartwatches simplify communication through convenient options:
Quick Replies: Predefined response options for messages.
Voice-to-Text: Convert voice messages to text for messages.
Voice Assistants (Siri, Google Assistant, Bixby, etc.)
Voice assistants enhance hands-free communication:
Siri (Apple): Apple’s voice assistant for iPhone integration.
Google Assistant: Google’s AI for Android users.
Bixby (Samsung): Samsung’s voice assistant for Galaxy devices.
Amazon Alexa: Available on certain smartwatch models.
13. Water Resistance and Durability
Different Levels of Water Resistance
Smartwatches vary in their water resistance capabilities:ater-Resistant: Can withstand minor splashes and sweat.
Waterproof: Resistant to water immersion to a certain depth and duration.
Swim-Proof: Suitable for swimming and water-related activities.
Dive-Proof: Can withstand deeper water immersion for scuba diving.
Durability Against Daily Wear and Activities
Smartwatches are designed to endure daily wear and tear:
Scratch Resistance: Durable materials and coatings protect against scratches.
Impact Resistance: Built to withstand accidental bumps and drops.
Corrosion Resistance: Resistant to damage from sweat and moisture.
Rugged Design: Some models are designed for outdoor and rugged activities.
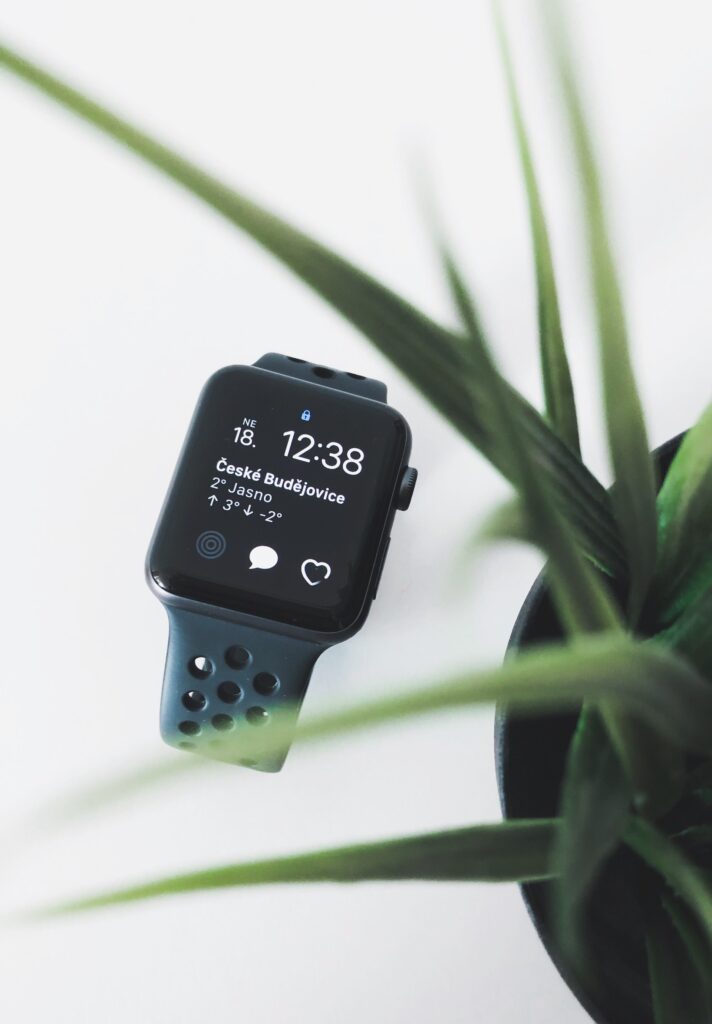
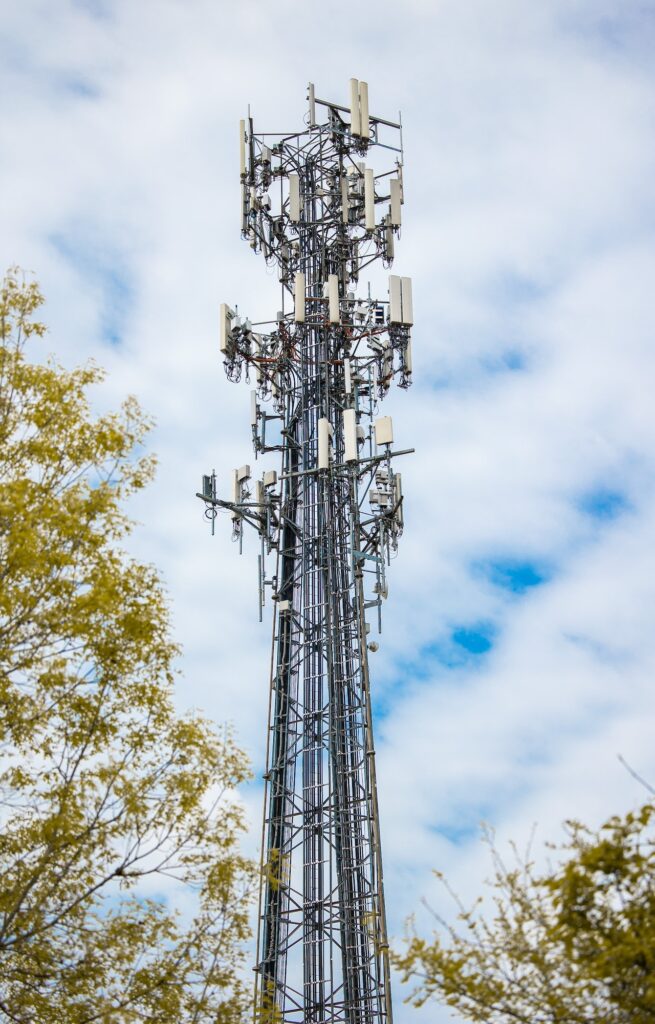


14. Navigation and GPS
GPS Tracking for Outdoor Activities and Navigation
Smartwatches offer GPS tracking for various outdoor activities:
Outdoor Workouts: Accurate tracking of running, cycling, hiking, etc.
Distance and Route: Measures distance covered and displays routes.
Altitude and Elevation: Provides elevation data for hikes and climbs.
Integration with Mapping and Navigation Apps
Smartwatches integrate with mapping and navigation apps:
Mapping: Display maps and routes directly on the watch screen.
Turn-by-Turn Directions: Provides step-by-step navigation guidance.
Offline Maps: Some watches allow downloading maps for offline use.
15. Entertainment and Media
Music Playback and Control
Smartwatches offer music playback features for on-the-go entertainment:
Music Storage: Some watches store music directly on the device.
Music Control: Play, pause, skip, and adjust volume from the watch.
Wireless Headphone Connection: Pair with Bluetooth headphones for wireless listening.
Compatibility with Streaming Apps and Services
Smartwatches provide compatibility with streaming apps:
Music Streaming: Control music playback from popular streaming services.
Podcasts and Audiobooks: Access and control podcasts and audiobook apps.
Offline Playback: Some watches allow downloading music for offline listening.
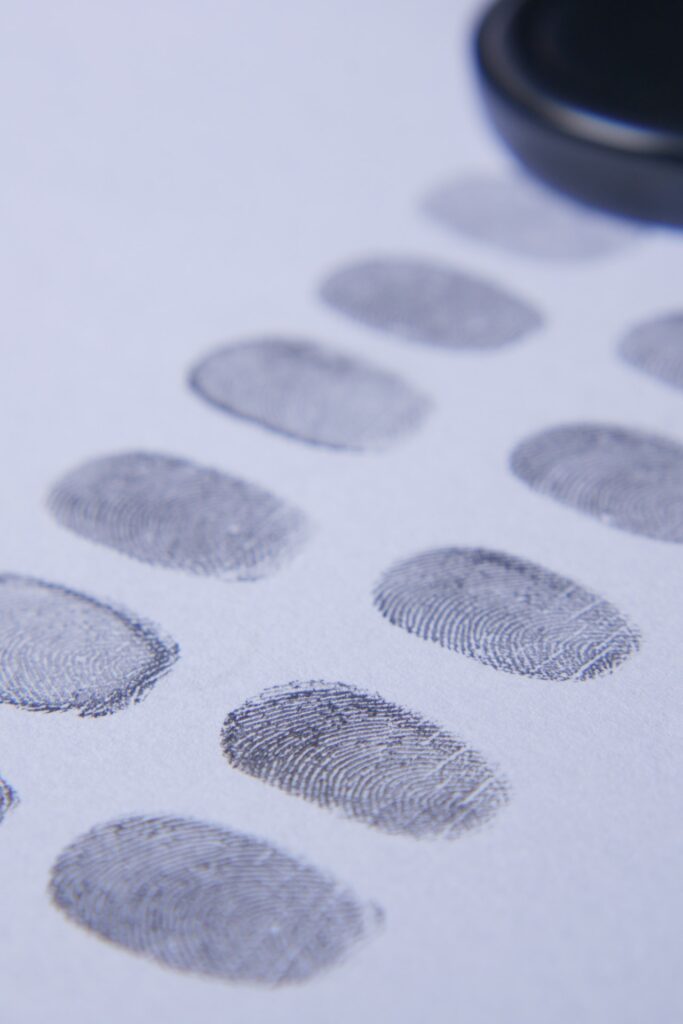


16. Security and Privacy
Biometric Authentication Methods
Smartwatches employ biometric authentication for enhanced security:
Fingerprint Recognition: Some watches have fingerprint sensors for unlocking.
Face Recognition: Cameras or sensors recognize the user’s face for access.
Data Privacy Considerations
Smartwatches address data privacy through various measures:
Data Encryption: Encrypted storage and transmission of sensitive data.
Permissions: Users control app permissions and data access.
Health Data: Some watches provide features to secure health-related data.
Data Syncing: Ensures secure transmission of data between watch and device.
17. Updates and Firmware
Importance of Firmware Updates for Improving Features and Security
Firmware updates play a crucial role in maintaining the functionality and security of smartwatches:
Enhancing Features: Updates can introduce new functionalities and improvements to existing features, enhancing the user experience.
Fixing Bugs: Updates address software bugs and glitches, ensuring smoother operation.
Security Enhancements: Updates patch vulnerabilities and security loopholes, safeguarding user data and privacy.
Compatibility: Updates ensure compatibility with new apps, devices, and technologies.
Performance Optimization: Updates optimize performance, ensuring the watch operates efficiently.

18. Cleaning & Maintenance
Cleaning and Maintenance Tips to Prolong the Lifespan of the Smartwatch
Proper care ensures the longevity of your smartwatch:
Regular Cleaning: Wipe the watch with a microfiber cloth to remove dirt and smudges.
Water Resistance: If water-resistant, ensure seals are intact and avoid exposing the watch to water beyond its rating.
Screen Protection: Apply screen protectors to prevent scratches.
Avoid Extreme Conditions: Keep the watch away from extreme temperatures and direct sunlight.
Charging: Charge the watch in a dry, well-ventilated area, and avoid overcharging.
Band Care: Clean bands and regularly check for wear or damage.
Software Updates: Keep the watch’s software updated for improved performance and security.
19. Future Trends and Innovations
Predictions About the Future of Smartwatches and Upcoming Trends
Smartwatches are poised to undergo exciting developments in the future:
Advanced Health Monitoring: Enhanced health sensors and medical-grade features for comprehensive health insights.
Wearable Ecosystems: Integration with other wearables like fitness trackers and smart clothing for holistic health tracking.
Form Factor Innovation: Introduction of flexible displays, slimmer designs, and novel shapes for improved aesthetics and comfort.
AI and Personalization: AI-driven insights and recommendations based on user behavior and health data.
IoT Integration: Deeper integration with smart home devices and the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem.
Battery Life Improvements: Focus on energy efficiency and longer battery life without sacrificing features.
Augmented Reality (AR) Integration: Incorporation of AR features for enhanced user experiences and information display.
Health-Related Applications: Expansion into telemedicine, remote health monitoring, and preventive health features.


